SSL Certificate (SSL certificate)Used on millions of websites to provide security for online transactions. However, during the implementation of SSL, some problems may occur, on the user’s screen accessing the website displaying an error message.
SSL connection error
An SSL connection error occurs during the process if you try to connect to an SSL enabled website and your browser (client – client) is unable to make a secure connection to the website’s server.
Depending on the cause of the SSL connection failure, the browser will display warnings like “This Connection is Untrusted“, “The site’s security certificate is not trusted“or”Your Connection is not private“.
Here Emergenceingames.com will guide you how to fix SSL connection errors.
Fix The SSL certificate for this website is not trusted
The Internet browser will display an error message saying that the website certificate is not trusted if the certificate has not been registered by a trusted certificate authority (CA). In order for a browser to accept a certificate, it must be associated with a “trusted root certificate”.
Trusted Root Certificates are embedded in popular browsers like Internet Explorer, Firefox, Chrome and Comodo Dragon. These root certificates are used as “trust tools” to verify the validity of all website certificates encountered by the browser. If a certificate is encountered that is not signed by one of these root certificates, the browser will report that it is an untrusted certificate and the visitor will receive the error message above.
Most trusted root certificates in the browser are recognized by the Certificate Authority (CA). When a CA signs a website’s certificate, the site’s certificate is associated with one of their trusted root certificates in the browser’s certificate store.
For security reasons, most CAs do not register the end-entity directly from the root certificate, instead they use the Intermediate certificate to create a “chain of trust” (chain of trust). trust) in the root certificate. In this system the root certificate will sign the Intermediate certificate and the Intermediate certificate is used to sign the certificates for individual websites.
So the “Untrusted” error is usually caused by one of the following two reasons:
– The website uses a self-signed certificate (Self Signed Certificate)
In many cases, the “Untrusted” error occurs because the website is using a self-signed certificate. As the name implies, a self-signed certificate is a certificate created and signed by a website owner using webserver software. Therefore, this certificate is not associated with any trusted root certificate in the browser’s certificate store and the browser will display an “Untrusted” error.
Self-signed certificates have many advantages. Firstly, this is a free generated certificate and works fine on internal servers. However, these certificates are not recommended for deployment on commercial sites.
– Intermediate certificate not installed
Another potential cause of the “Untrusted” error is that the site administrator did not correctly install all the Intermediate certificates on their webserver. Here is an example of this error:
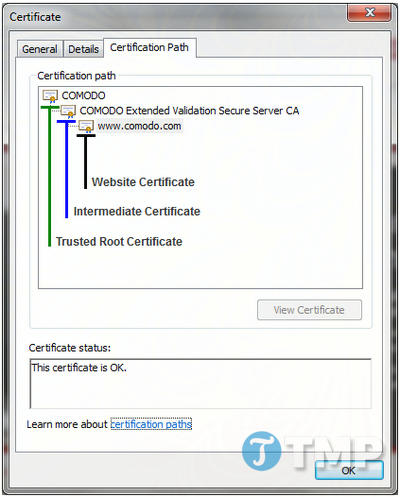
In the above diagram you can see the certificate for www.comodo.com
When a visitor makes a connection to www.comodo.com
Most digital certificate (CA) providers will send a CA bundle file containing all the required Intermediate certificates and end-entity to the website owner. However, if the webserver’s Admin does not install all the Intermediate certificates, the user will receive the error message “certificate not trusted”.
Certificate Name Mismatch error
The “Certificate Name Mismatch” error occurs when the server displaying the domain name listed on the SSL certificate does not match the domain name to which the browser is connected. To initiate an HTTPS session, the domain name on the certificate must exactly match the domain name in the browser’s address bar.
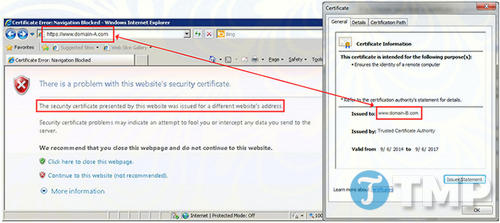
Here are some causes of the error:
– The website/server is accessed using an internal hostname or IP address, but the certificate is only issued with a fully qualified domain name (such as www.domain.com
– The certificate issued is domain.com, but in the browser address bar entered as www.domain.com
However, if you are facing the “Certificate Name Mismatch” error, this could be the cause of the error. Using certificates Wildcards can help you fix this SSL connection error that occurs because any and all subdomains of domain.com are automatically protected.
– Error Certificate Name Mismatch can happen when multiple websites are hosted on the same IP address. This often happens in many shared hosting environments. In a normal HTTP connection, the browser tells the server which domain it wants to connect to with the host header.
However, when an HTTPS connection is made, the SSL handshake means that the browser requests a certificate from the server before presenting the host header. As a result, the server doesn’t have the information it needs to decide which certificate to send and will present the wrong certificate.
IfThere is only one website and one certificate on one IP address, the cause of the error is not here. However, if there are multiple websites located on the same IP address, the server may provide a certificate for the wrong domain. To prevent this situation users can use Multi-Domain certificates, which allows website owners to add all websites and hostnames to the Subject Alternative Name (SAN) frame field of the certificate.
Mixed content error
For a secure connection, HTTPS is established, the items on the page must be obtained from a secure source. That is, all images, videos, iframes, flash movies and Javascripts must be sourced from safe sources. If any of the items are not taken from a safe source, site visitors will receive an error message similar to the one below:
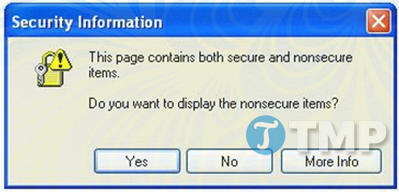
If the visitor chooses Yes, all entries will be displayed, but the connection will return to an unsecured HTTP connection. If you choose No then only safe items will be displayed. That is, certain videos and images will not be displayed or the page will not execute important scripts. Either way, this is a bad signal to your website visitors.
Here’s how website administrators can fix SSL connection errors Mixed content:
– Do not call any insecure content through HTTP or port number 80. Change all references from HTTP to HTTPS. Make sure you have SSL set up on the source location. If you use a sub-domain to host your website elements, a Wildcard certificate may be of help to you.
– Use relative links on your site instead of absolute links. For example, instead of using src = http://mydomain.com/my-script.jsyou can use scr = / my-script.js. If your homepage is accessed via HTTPS, the browser will load /my-script.js via HTTPS. This technique is also useful if your site references external content that is server-side via HTTP (like YouTube or Google Analytics, for example).
– Deploy SSL across your entire site. This is to ensure a better level of security for your website visitors, and this is also the criteria that Google uses to rank website rankings, improving SEO somewhat.
Note that implementing SSL on your entire site means you have 2 copies of your content, so you’ll have to “tell” search engines which version is authoritative. To do this thing:
Tell search engines which HTTPS version is authoritative by updating the link to point to the HTTPS version. Update XML sitemap to reference the HTTPS version of your assets. Making these changes means that search engines will index the SSL version of your website and show it in search engine results.
+ Guaranteed robots.txt available over HTTPS.
+ Redirect all HTTP requests to the HTTPS version with a permanent 301 redirect. That is, your search engine page rankings will be transferred to the HTTPS version.
+ Update webmaster tools to reference the HTTPS version of your site instead of HTTP.
Above Emergenceingames.com has just introduced and guided you some ways to fix SSL connection errors. If you are facing an SSL connection error, readers can apply one of the above ways to fix the error.
Besides common SSL errors, when you visit some popular websites like Facebook, Gmail can also fall into this situation. In this case, how to fix SSL errors when entering Facebook, Gmail that Emergenceingames.com can help you connect again.
https://thuthuat.Emergenceingames.com/khac-phuc-loi-ket-noi-ssl-26246n.aspx
If you have any questions, you can leave your comments in the comment section below the article!
Related keywords:
Fix SSL connection error
SSL connection error, SSL connection fix,
Source link: Fix SSL connection error
– Emergenceingames.com



