802.11ac was introduced in 2013 and you’ll find it on smartphones, laptops, computers and smart TVs. The 802.11ac standard builds on the successful 802.11n standard introduced in 2007 and offers a number of major benefits. In the article below, Free Download will show you the differences between 802.11ac and 802.11n Wifi standards, as well as how to get the best results from your current wireless signal.
The specifications that users look for when buying any device are hardly anything new: from screen size, resolution, megapixels, memory size and processing speed, … But one of the most important and “abandoned” by users is WiFi and the latest standard is 802.11ac. Therefore, we need to compare the differences between 802.11ac and 802.11n Wifi standards to understand the advantages and disadvantages of these two standards.
Compatibility – Everything works together
The good news for you is that 802.11ac-capable chipsets are fully backward compatible with previous Wi-Fi standards.

This means it works perfectly with 802.11a (introduced in 1999), 802.11b (2000), 802.11g (2003) and 802.11n (2007).
The bad news, however, is that you’ll be limited in the performance of the older standard and will only get the full benefit of Wireless AC or Wifi AC Wifi if you’re connecting from 802.11ac to 802.11ac. That means an 802.11ac router and an 802.11ac device.
So what are the benefits of the 802.11ac standard?
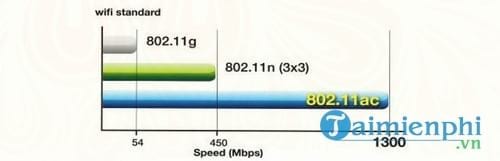
802.11ac and 802.11n . speeds
You’ve probably noticed the 6-year gap between 802.11n and 802.11c. These are technological terms, and the big benefit that 802.11ac brings is speed.
Wifi is always “advertised” to use “theoretical” speeds, and this 802.11ac standard has a speed of 1300 megabits per second (Mbps), which is equivalent to 162.5 megabytes per second (MBps). This is 3 times faster than 802.11n’s 450Mbps.
The speed issue here is garbage data. In the real world, no one is using the theoretical speeds, and the fastest 802.11ac real world speed recorded in the test was around 720Mbps (90MBps). In contrast, 802.11n achieves speeds of 240Mbps (30MBps).
But there’s a more important part to understanding your real-world experiences: antennas.
Long-term 802.11ac has headroom to support up to 8 antennas each running at over 400Mbps, but the fastest routers only have 4 antennas. The reason is because antennas cost more, take up space, and are smaller than devices with fewer antennas that would make no sense to add to the router. Specifically:
– Smartphone: 1 antenna
– USB Adapters: 1 or 2 antennas
– Tablet PC: 2 antennas
– Laptop: 2 antennas (sometimes on computers it is 3)
– Computer: 3 or 4 antennas (PCI Express EXPR +1.31% cards)
If your 802.11ac router is being connected to a single antenna 802.11ac smartphone then 400Mbps (50Mbps) is theoretical maximum and 200Mbps (25MBps) is practical.
This speed has been reduced but is still faster than most home broadband connections and is only the limit between transferring files wirelessly between devices on your local network (e.g. laptop to laptop or laptop). computer to the NAS).
Moreover, 802.11n only supports up to 4 antennas with a speed of 100 Mbps (12.5MBps), so when you do calculations for devices using 802.11n antennas the distance begins to expand. Especially when it comes to 802.11ac’s next big benefit.

802.11ac and 802.11n . range
AC Wifi is much faster but its peak speed is not really the selling point. That’s speed at long range.
First the bad news: 802.11ac Wi-Fi doesn’t really reach any farther than 802.11n Wi-Fi. In fact, 802.11ac uses the 5GHz band and 802.11n uses the 5GHz and 2.4GHz bands. The higher bands are faster but the lower bands go further.
The difference in signal strength between 802.11ac on 5GHz and 802.11n on 5GHz and 2.4GHz is minimal.
Why? The first is because the 2.4GHz frequency is used on everything from cordless desktop phones to microwave ovens, and the 5GHz frequency remains largely free interference for a cleaner signal.
The second key element is beamforming. Usually the wireless signal is simply thrown out of your router in all directions equally, like ripples when you throw a rock into the water. This is why you should place the router near a central location at home or office and as high as possible.
Beamforming is different. It’s built into the 802.11ac specification and is a “smart signal” that detects where a connected device is and boosts the signal strength in the direction of these signals. However, you should still “position” your router in a central location.
All of this means that 802.11ac performance is far better maintained than 802.11n. Peak performance can be up to 3x, but somewhere between 5-10x the speed benefits are not unusual and this is where 802.11ac comes in. Here are some examples:
– 802.11ac at 1m: 90MBps, 10m: 70MBps and 20m behind two hard walls: 50MBps
– 802.11n at 1m: 30MBps, 10m: 20MBps and 20m behind two hard walls: 5-10MBps.
These numbers are of course a general guide and there will be examples of more specific 802.11ac devices for you to choose from.

802.11ac and 802.11n: Availability and Pricing
Technology is a wonderful thing. If 12 months ago, finding 802.11ac devices was difficult and extremely expensive. Now 802.11ac is integrated into high-end smartphones, tablets, laptops and smart TVs, and even in mid-range devices.
There are three reasons to explain this. The first is the obvious performance benefits, especially for single-antenna devices like smartphones. The second is more battery efficient because Wifi needs to work less during data transfers to be able to complete faster. The third is that widespread economies of scale cause prices to fall.
Note: make sure you find officially certified devices (use the official Wifi logo logo). Some devices still use 802.11ac “drafts” and while these tend to work well, ultimately it is not guaranteed.
There’s no difference between 802.11ac and 802.11n when it comes to price, most of the devices you buy already have 802.11ac built in, so you won’t have to pay extra.
There are still cases where the price “spikes”, but it is the routers (routers). Wireless AC routers still tend to have a 20-50% charge (depending on model), but because “old” routers run the risk of clogging up any home Internet connection, office, ….
Recommend some 802.11ac
Like any area of technology, the market is always changing, but the following 802.11ac recommendations are the top recommendations for the 802.11ac standard.
Best price router
D-Link DIR-880L – $180 – current price/performance. Although the D-Link DIR-880L lacks an integrated modem, it is capable of boosting your Wifi network at a fraction of the cost of the competition.
Routers with the best performance
Netgear R7500 Nighthawk X4 – $280 – The first in the next wave of ‘AC2350’ routers (1300 Mbps AC Wi-Fi connecting to 600 Mbps WiFi N and pooled). It will cost you quite a bit and combine with a PC PCI adapter to get the best experience from the Netgear R7500 Nighthawk X4 .
Best Peripherals
Asus PCE-AC68 PCI Adapter – $99- If you want the fastest wireless experience possible, this is the beast you’re looking for. Keep an eye out for PCE-AC87, Asus will be rolling out ‘AC2350’ routers soon, and this should be more than enough for most users.
Best USB Adapter
The D-Link DWA-171 costs $24 – has a dual antenna faster than the AC1200 USB dongle, which is pretty fast while the DWA-171 is slower. The D-Link DWA-171 is so small that you can plug it in your laptop at all times, and the performance the D-Link DWA-171 delivers is quite “powerful”.
https://thuthuat.Emergenceingames.com/su-khac-nhau-giua-chuan-wifi-802-11ac-va-802-11n-23637n.aspx
In addition, if you are learning between RJ45 and RJ48 network ports, you can follow the article Compare RJ45 and RJ48 . network ports here
Author: Nguyen Hai Son
4.0– 15 evaluate)
Related keywords:
802.11ac Wi-Fi standard
802.11n Wifi standard, compare 802.11ac and 802.11n Wifi standards,
Source link: Differences between 802.11ac and 802.11n Wi-Fi standards
– Emergenceingames.com
